Tools
FL4Deep
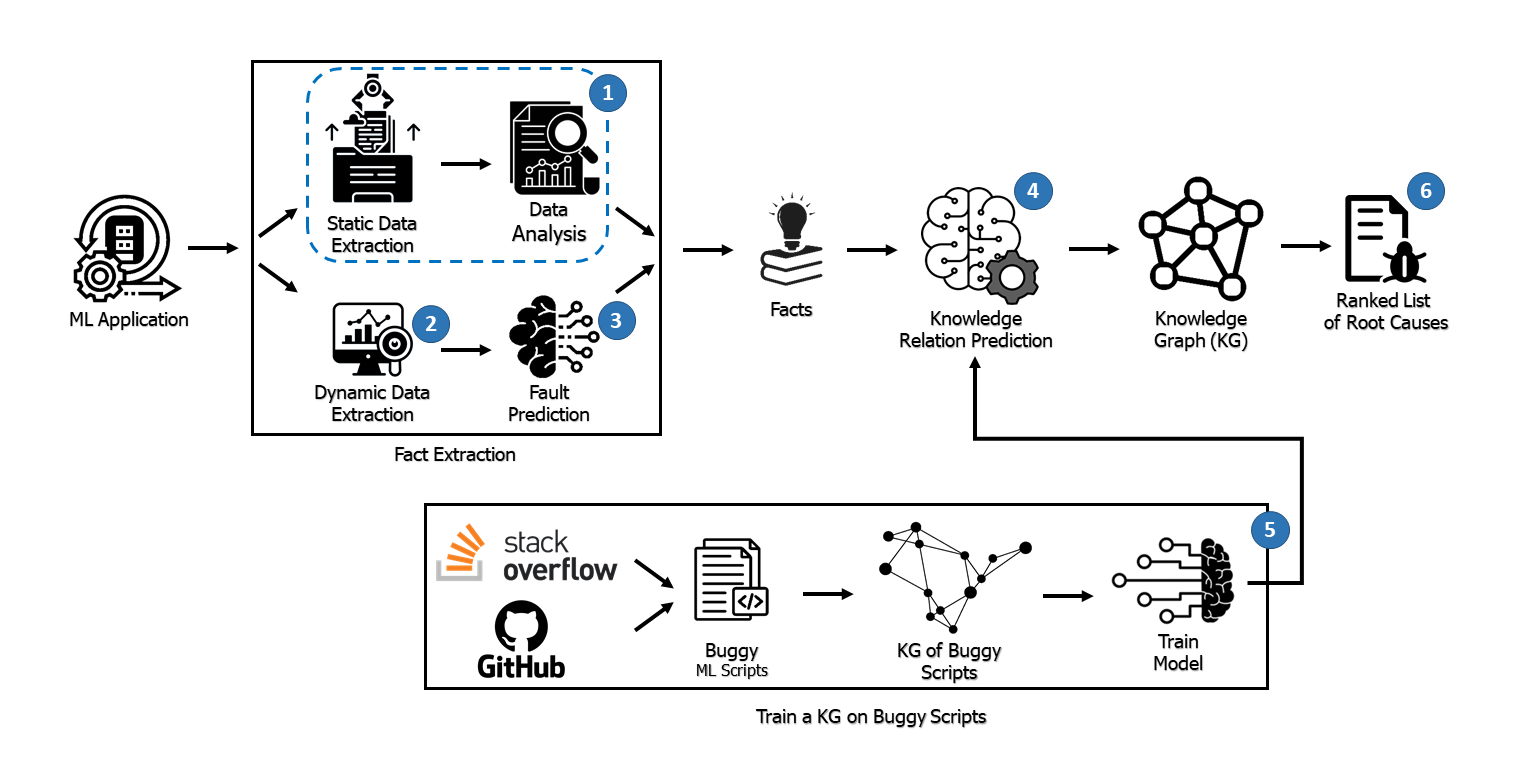
While the DL model is central to DL components, there are numerous other elements that significantly impact the performance of DL components. As a result, fault localization methods that concentrate solely on the DL model overlook a large portion of the system. To address this, we introduce FL4Deep, a system-level fault localization technique based on a Knowledge Graph (KG). Link
NeuraLint
A DL program encodes the network structure of a desirable DL model and the process by which the model learns from the training dataset. Like any software, a DL program can be faulty, which implies substantial challenges of software quality assurance, especially in safety-critical domains. It is therefore crucial to equip DL development teams with efficient fault detection techniques and tools. To this end, we propose NeuraLint, a model-based fault detection approach for DL programs, using meta-modelling and graph transformations. Link
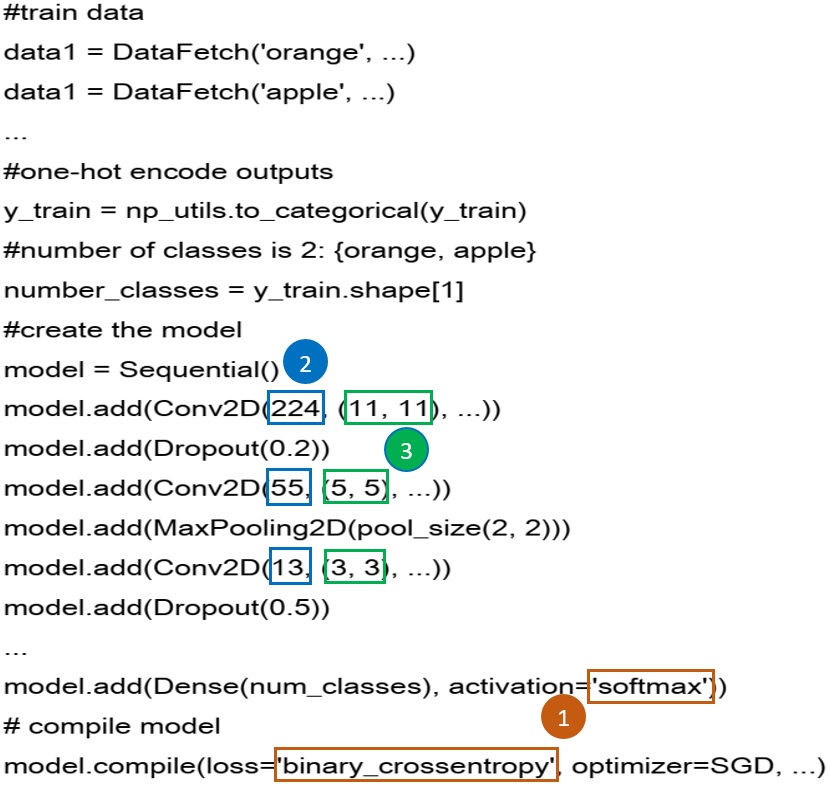
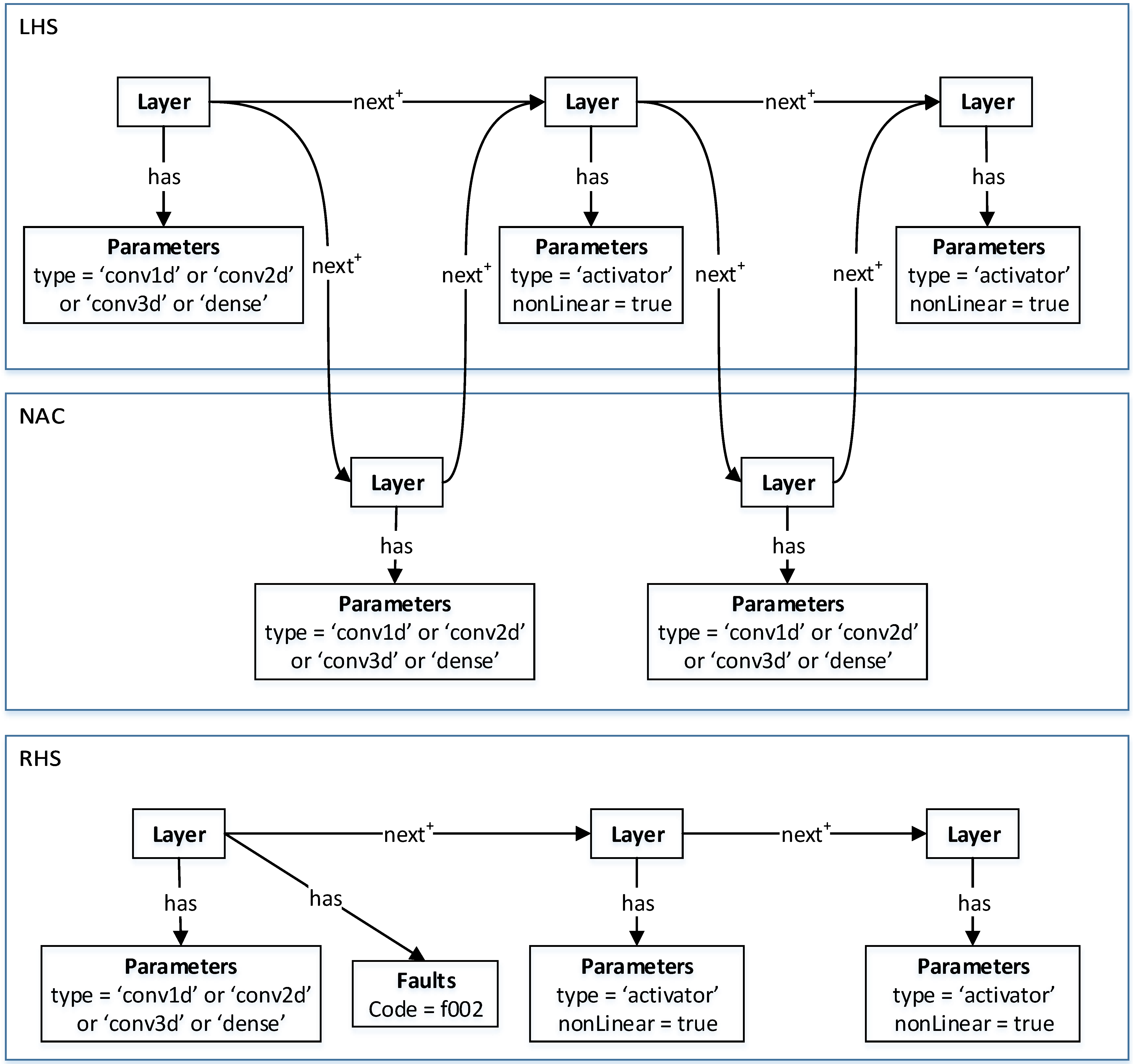
DRLinter
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) is the application of DL in the domain of Reinforcement Learning (RL). Like any software system, DRL applications can fail because of faults in their programs. To allow for the automatic detection of faults in DRL programs, we have defined a meta-model of DRL programs and developed DRLinter, a model-based fault detection approach that leverages static analysis and graph transformations. The execution flow of DRLinter consists in parsing a DRL program to generate a model conforming to our meta-model and applying detection rules on the model to identify faults occurrences. Link
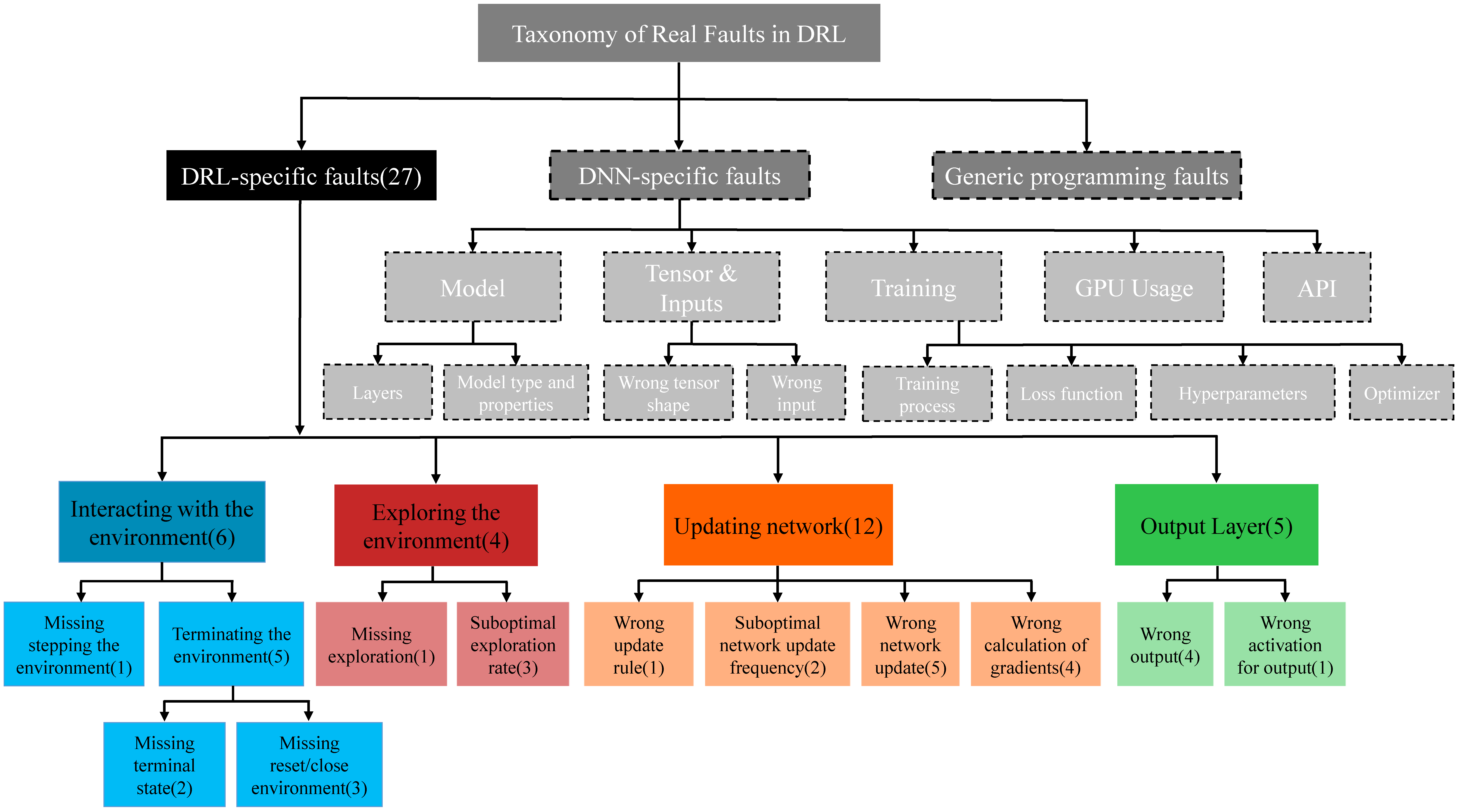
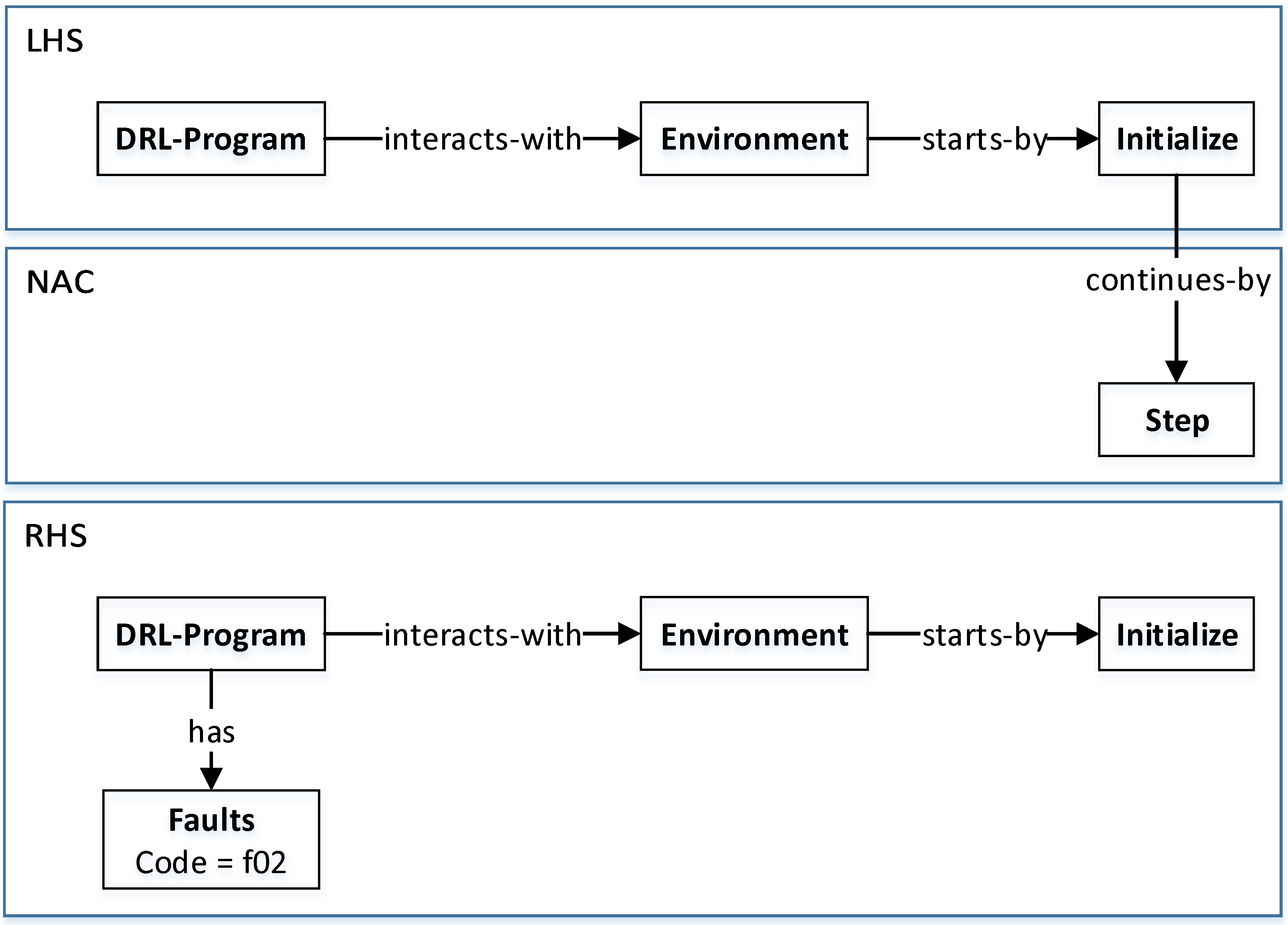
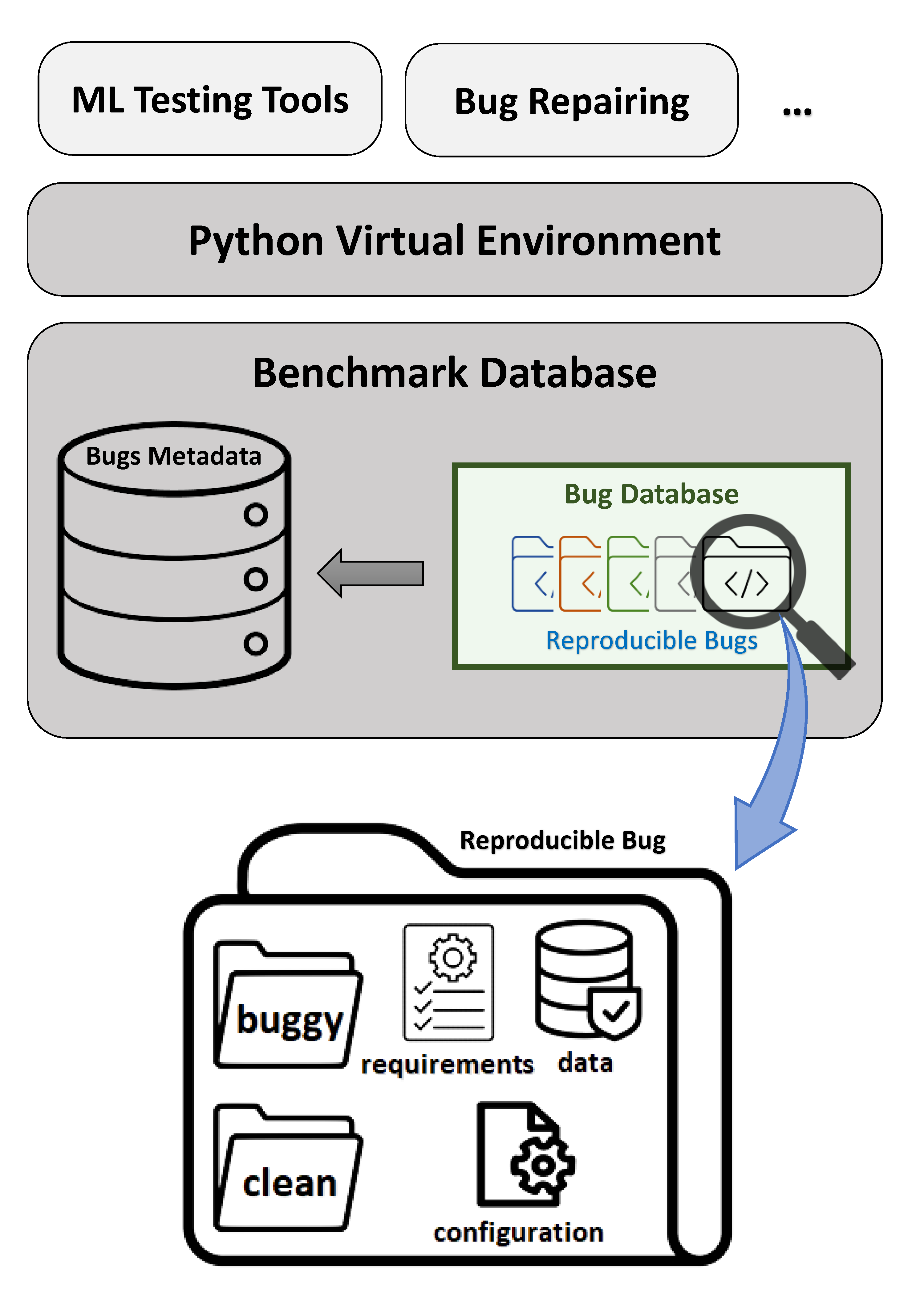
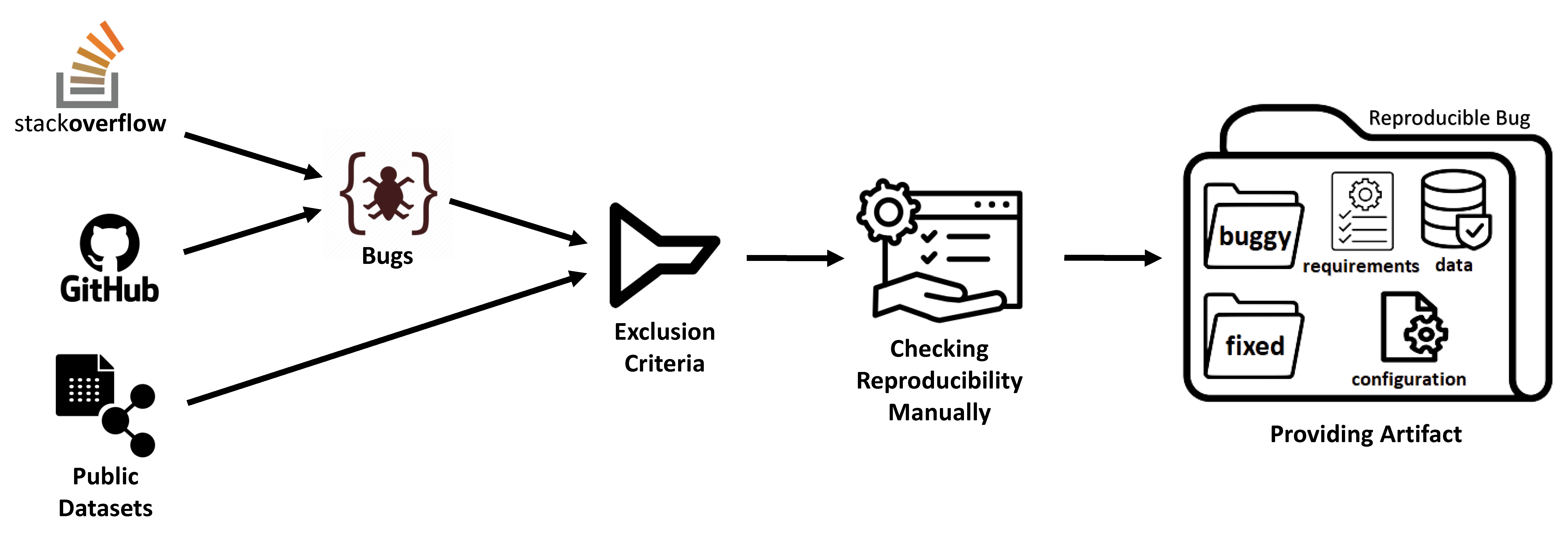
defect4ML
Although most of tools working on the quality assurance of ML-based systems use bugs’ lifecycle, there is no standard benchmark of bugs to assess their performance, compare them and discuss their advantages and weaknesses. To this end, we explore the challenges of generating a benchmark of bugs in ML-based software systems and provide a bug benchmark namely defect4ML that satisfies all criteria of standard benchmark, i.e. relevance, reproducibility, fairness, verifiability, and usability. Link